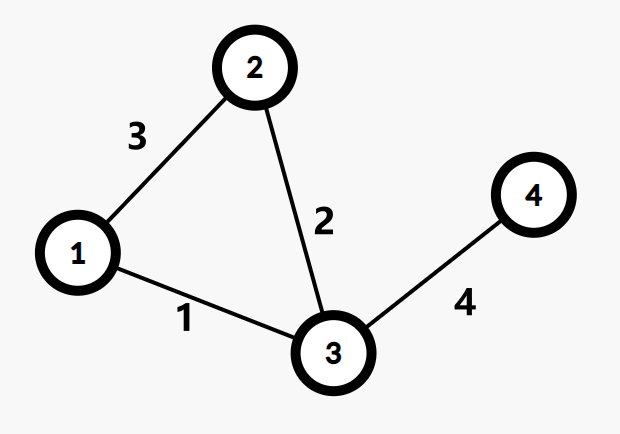
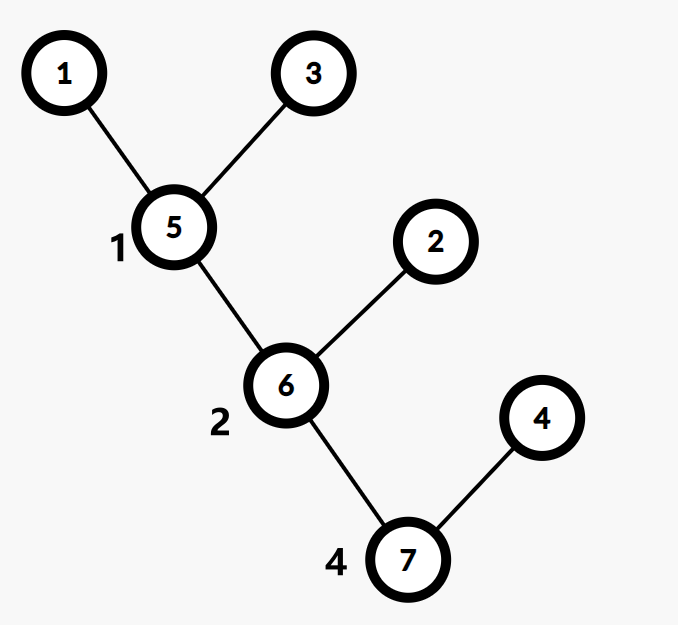
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=2e5+10;
const int maxm=4e5+10;
const ll INF=5147483647;
int T,n,m,q,k,s,cnt;ll lastans;
int f[maxn*2],lg[maxn];
int depth[maxn*2],fa[maxn*2][31];
struct node{
int u,v,l,a;
}e[maxm];
struct road{
int to,cost;
};
struct power{
ll w,l;
}p[maxn*2];
vector<road> mp[maxn];
vector<int> tree[maxn*2];
typedef pair<ll,int> Pair;
void _clean()
{
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
memset(depth,0,sizeof(depth));
for(int i=0;i<=cnt;i++)
for(int j=0;j<=30;j++)
fa[i][j]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)mp[i].clear();
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)tree[i].clear();
cnt=0;lastans=0;
}
void makelog()
{
for(int i=1;i<=maxn;i++)
lg[i]=lg[i-1]+(i==1<<(lg[i-1]+1));
return;
}
bool cmp(node x,node y)
{
return x.a>y.a;
}
int Find(int x)
{
if(x==f[x])return x;
return f[x]=Find(f[x]);
}
void kruscal()
{
sort(e+1,e+m+1,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=n*2;i++)f[i]=i;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
if(cnt==2*n-1)break;
int x=Find(e[i].u),y=Find(e[i].v);
if(x==y)continue;
cnt++;
f[x]=f[y]=cnt;
tree[cnt].push_back(y);
tree[cnt].push_back(x);
p[cnt].w=e[i].a;
}
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)p[i].l=INF;
return;
}
void dij()
{
priority_queue<Pair,vector<Pair>,greater<Pair> > q;
bool vis[maxn];ll dis[maxn];
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)dis[i]=INF;
dis[1]=0;
q.push(make_pair(0,1));
while(!q.empty())
{
int x=q.top().second;
int c=q.top().first;
q.pop();
if(vis[x])continue;
vis[x]=true;
for(int i=0;i<mp[x].size();i++)
{
if(dis[mp[x][i].to]>dis[x]+mp[x][i].cost)
{
dis[mp[x][i].to]=dis[x]+mp[x][i].cost;
q.push(make_pair(dis[mp[x][i].to],mp[x][i].to));
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)p[i].l=dis[i];
return;
}
void dfs(int now,int father)
{
depth[now]=depth[father]+1;
fa[now][0]=father;
for(int i=1;i<=lg[depth[now]];i++)
fa[now][i]=fa[fa[now][i-1]][i-1];
for(int i=0;i<tree[now].size();i++)
{
dfs(tree[now][i],now);
p[now].l=min(p[now].l,p[tree[now][i]].l);
}
return;
}
ll ask(int x,int y)
{
for(int i=lg[depth[x]];i>=0;i--)
if(p[fa[x][i]].w>y)x=fa[x][i];
return p[x].l;
}
int main()
{
makelog();
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
cnt=n;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&e[i].u,&e[i].v,&e[i].l,&e[i].a);
mp[e[i].u].push_back((road){e[i].v,e[i].l});
mp[e[i].v].push_back((road){e[i].u,e[i].l});
}
kruscal();
dij();
dfs(cnt,0);
scanf("%d%d%d",&q,&k,&s);
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
int x,y;scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
int vx=(x+k*lastans-1)%n+1;
int py=(y+k*lastans)%(s+1);
lastans=ask(vx,py);
printf("%lld\n",lastans);
}
_clean();
}
return 0;
}
|